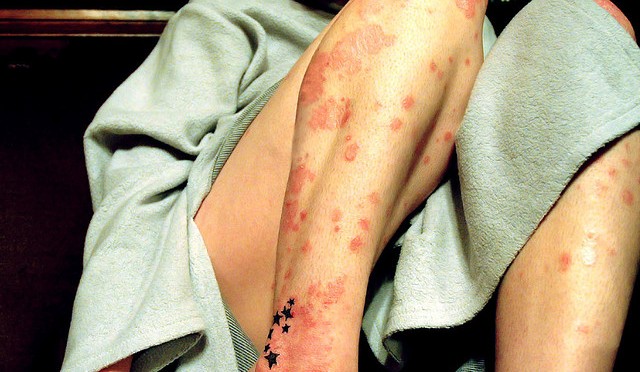
Psoriasis is an inflammatory skin condition that results in itchy and dry patches of skin on the sufferer. Affecting around 2 to 4% of
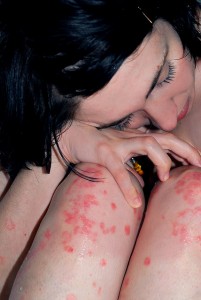
Western populations, psoriasis has many risk factors, including family history, diet, obesity, stress, and alcohol consumption patterns.
Various vitamins and other individual dietary components such as Vitamins A, E, C, D, and other fatty acids have been studied for their potential benefits for psoriasis risk, though the influence a particular diet as a whole (like the Mediterranean diet) is much less known.
A new study published in the Journal of Translational Medicine examined associations (if any) between adherence to the Mediterranean diet and severity of psoriasis in Italian adults.
62 patients admitted to the Department of Clinical Medicine and Surgery at the University of Naples Federico II in Italy were recruited for this study. 42 men and 13 women made up the participant pool, with an average age of 50.2 years (+/-10.5yrs). A control group consisting of 62 age-, gender-, and BMI-matched healthy individuals were used as controls.
Adherence to the Mediterranean diet was determined using self-reported questionnaires.
Severity of psoriasis was determined by physician diagnosis, and given a standardized Psoriasis Area and Severity Index score (PASI). C-reactive protein (CRP) and body composition were also determined for each participant.
Important Findings:
Continue reading Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet Associated with Lower Risk of Psoriasis